Openstack#
OpenStack is an open-source cloud operating system consisting of various components which handle virtualised compute resources. We use an OpenStack environment for the cloud infrastructure service to provide resources to our users.
In order to work with your cloud infrastructure, we will set up an OpenStack “tenant” with a unique identiifer for your company or your project. In OpenStack, a tenant is a logical group of users and resources that are isolated from other tenants. Each tenant has its own set of users, who can launch virtual machines, manage networks and storage resources. Please contact us first for an individual offer via office@eodc.eu. After finding a suitable package for you and once your tenant is setup, please create an EODC account following this link. Upon confirmation the EODC OpenStack launcher will give you full control over your resources.
Accessing your tenant is either possible via the OpenStack Dashboard or via the OpenStack API.
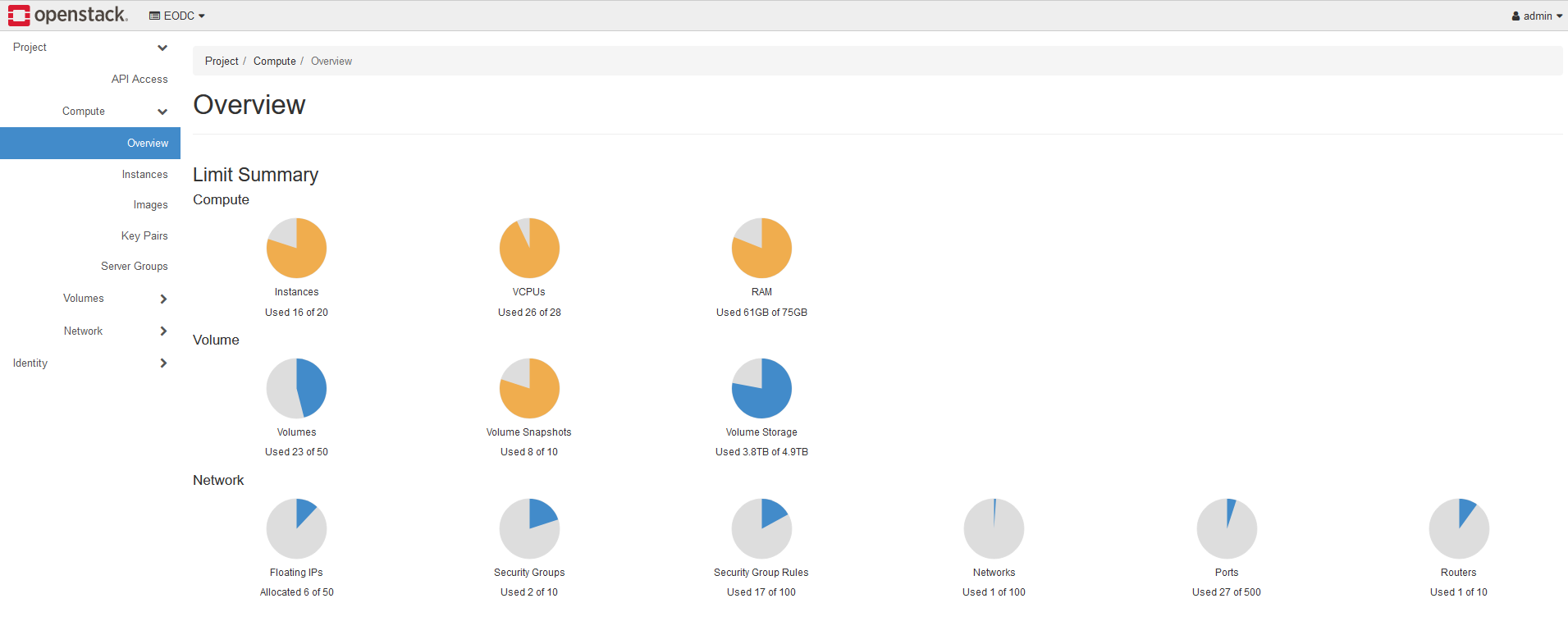
As a preview, you can see how the Dashboard looks like below:
Distributions available in our openstack cloud.eodc.eu:#
RedHat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) based:#
Rocky Linux 8
Debian based:#
Debian 11
Ubuntu22.04LTS
Distributions available in our openstack launcher.eodc.eu:#
RedHat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) based:#
Almalinux8
CentOS7
CentOS stream
Debian based:#
Debian 10
Ubuntu16.04 LTS
Ubuntu18.04 LTS
Ubuntu20.04 LTS
Usecases#
In reality there is no good or bad distribution. Which distro one uses is mostly personal preference and familiarity. The most notable difference would be the package manager which is
aptfor Debian based distrosdnffor RHEL based distros
Another difference is the availability of packages through said package managers.
Debian has a lot of packages in it’s main repositories while RHEL is rather limited though it can alway be expanded by adding new repositories like epel release.
Further the differences between Debian based distros like Debian and Ubuntu are even less. It mostly comes down to preinstalled packages. Or like in the case of Ubuntu the proprietary package manager snap which is used in addition to apt. The same applies to RHEL based distros like Almalinux or CentOS.
Getting started#
How to launch an instance can be found in our old knowledgebase. How to add a SSH key and connect via SSH is also covered there.
Important: On cloud.eodc.eu the default user is eodc. On launcher.eodc.eu it is the image name of the used distribution i.e. ubuntu or centos.
